Definition. Idiopathic sporadic ataxia with positive serum antigliadin antibodies (IgG and/or IgA), even in the absence of duodenal enteropathy.
Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT or A-T), also referred to as ataxia-telangiectasia syndrome or Louis–Bar syndrome, is a rare, neurodegenerative, autosomal recessive disease causing severe disability.
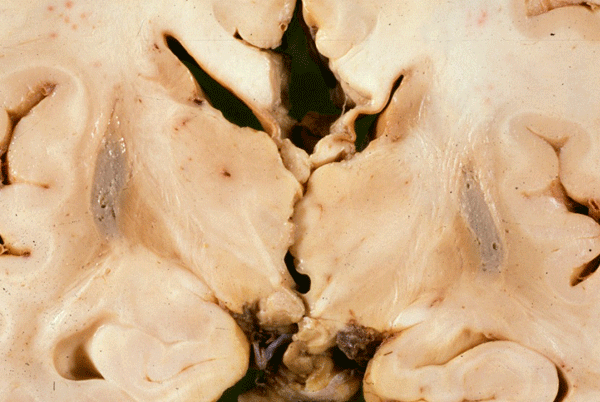
The ataxias are clinically heterogenous disorders caused by pathological processes affecting the cerebellum and cerebellar pathways resulting in impaired coordination.
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that includes gait abnormality.Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum.

Grant Type LOI Deadlines Application Deadlines Maximum Budget (in US dollars) General Research Grant: Feb 1 & July 15: April 1 …

Ataxia Telangectasia AT Mutant (ATM) gene ; Chromosome 11q22.3; Recessive Epidemiology Incidence: 1 in 40,000-300,000 live births: …
The Massachusetts General Hospital Ataxia Unit provides expert diagnosis, treatment and education for patients with ataxia and other cerebellar disorders.
INTRODUCTION. Acute cerebellar ataxia is a syndrome that occurs in previously well ren, often presenting as a postinfectious disorder [].The pathogenesis, clinical presentation, evaluation, and prognosis of acute cerebellar ataxia will be reviewed here.


What is FA? Friedreich’s ataxia (FA) is a debilitating, life-shortening, degenerative neuro-muscular disorder. About one in 50,000 people in the United States have Friedreich’s ataxia.

Epidemiology Western Europeans Incidence: 1 in 20,000 to 125,000 Carrier frequency: 1 in 60 to 110 75% of hereditary ataxia with onset < 25 years