
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers, based on aliphatic or semi-aromatic polyamides.Nylon is a thermoplastic silky material that can be melt-processed into fibers, films or shapes.

The permeability and solubility of gases and liquids in a polymer can be very different for different polymers and permeants. In general, permeability and solubility at a given temperature depend on the degree of crystallinity (morphology), the molecular weight, the type of permeant and its concentration or pressure, and in the case of
First and foremost, unlike other 3D printing technologies, all of the materials we use in our Augmented Polymer Deposition (APD) 3D printing process are completely safe to use in your office, without any special venting, disposal equipment or gloves, and are environmentally friendly.
Polyamide fabric, also known as nylon fabric, is a form of plastic.Polyamide fabric, like polyester fabric, is a polymer. It is manufactured through a chemical process. In short, high amounts of heat and pressure are applied to fossil fuels to yield sheets of polyamide and nyl
.jpg)
The microstructure of a polymer (sometimes called configuration) relates to the physical arrangement of monomer residues along the backbone of the chain. These are the elements of polymer structure that require the breaking of a …
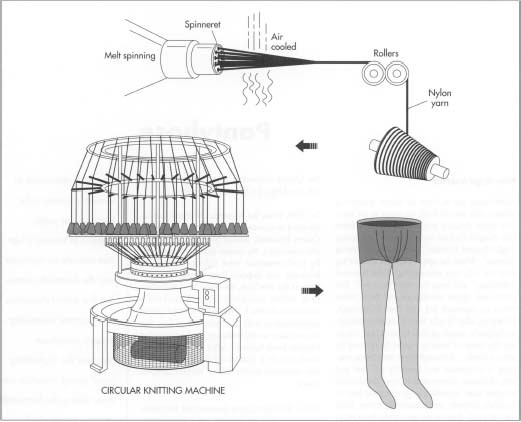
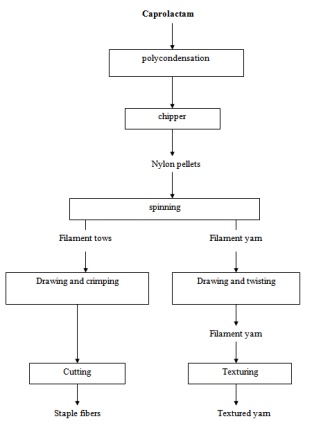
Polymer Processing including spinning of polymer, spinneret and extrusion process with detail of various types of spinning process

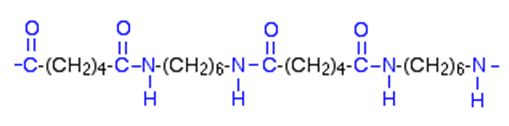

Polymers 1. Introduction. Prior to the early 1920’s, chemists doubted the existence of molecules having molecular weights greater than a few thousand.

May 24, 2008 · I have been trying to find out what the Glock and other polymer pistol frames are made of. A few places have said that the Glocks frame is made of polymer …
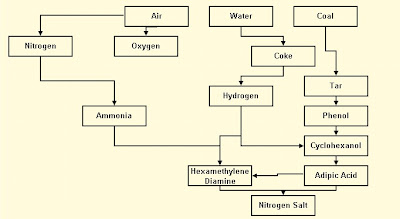
Polymers formed in this way, where both ends of the growing chain have functional groups which can react with a monomer or with the appropriate functional group on another chain, are called step-growth polymers.
Polymer definition, a compound of high molecular weight derived either by the addition of many smaller molecules, as polyethylene, or by the condensation of many smaller molecules with the elimination of water, alcohol, or the like, as nylon.